
DOT Compliance Checklist: Connect Express LLC
As dawn breaks over a bustling freight yard, fleets of flatbed trucks stand ready for the day’s challenges. Yet, unseen regulatory pitfalls threaten to disrupt even the most well-prepared operations.
Ensuring compliance with the myriad of Department of Transportation (DOT) standards is a formidable task for any trucking professional. Overlooking even a single regulation can result in substantial penalties or operational setbacks.
Navigating the complexities of DOT compliance requires a comprehensive checklist that covers every facet of operation, from equipment standards to driver qualifications. Without such a roadmap, the risk of non-compliance looms large, jeopardizing the smooth conduct of day-to-day activities.
Understanding DOT Regulations
The Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations represent a complex legal framework integral to the horizontal logistics landscape, particularly in the realm of flatbed trucking. Mastery of these rules isn’t just about legal compliance—it’s an exercise in safeguarding the welfare of drivers, the public, and the goods being transported. Each component of these regulations is devised to address a specific risk or set of risks, making thoroughness a requisite for their navigation and implementation.
Adherence to DOT guidelines is akin to a delicate ballet—every step must be precise and every movement deliberate. This isn’t just about ticking boxes on a compliance checklist; it’s a continuous endeavor to align with an ever-evolving array of safety standards, operational procedures, and administrative tasks. With this in mind, the ultimate DOT Compliance Checklist becomes your guide to operating with distinction, ensuring that each mile traveled is a testament to your commitment to excellence and regulatory adherence.
Essential DOT Rules Overview
Navigating DOT regulations requires profound understanding—particularly for the flatbed trucking sector.
Effective January 6, 2020, the DOT Clearinghouse database is mandatory for all CDL drivers’ employment verification.
Compliance ensures not just adherence to legal frameworks but also embodies a commitment to the highest safety and ethical standards, with every haul reflecting the calibre of your operation.
Key Legal Requirements
Adhering to DOT regulations is critical for maintaining lawful operations and ensuring road safety.
- Commercial Driver’s License (CDL): Ensure all drivers hold a valid CDL appropriate for the vehicle class and cargo.
- Medical Certificates: Maintain current medical certificates for all drivers as proof of fitness for duty.
- Hours of Service (HOS) Compliance: Follow HOS rules to prevent driver fatigue; utilize Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) where required.
- Vehicle Maintenance: Perform routine inspections, maintenance, and necessary repairs as dictated by FMCSA regulations.
- Drug and Alcohol Testing: Enroll in a DOT-compliant drug and alcohol testing program, including pre-employment, random, and post-accident testing.
- Hazardous Materials (HAZMAT): Obtain proper endorsements for HAZMAT transport and adhere to specific handling and documentation protocols.
- Cargo Securement: Abide by DOT standards for properly securing all types of cargo, paying close attention to flatbed-specific requirements.
- Insurance Requirements: Carry adequate insurance coverage conforming to DOT minimum requirements for liability and cargo.
- DOT Number and MC Authority: Maintain up-to-date registration with a DOT number and, if necessary, Motor Carrier (MC) operating authority.
- Unified Carrier Registration (UCR): Participate in the UCR program if operating across state lines.
- International Registration Plan (IRP) and International Fuel Tax Agreement (IFTA): Register with both IRP and IFTA for apportioned tax compliance.
Non-compliance can lead to substantial fines, operational disruptions, and reputational damage.
Efficient compliance management is a hallmark of professionalism, fostering trust with clients and regulatory bodies alike.
Driver Qualification Files
It’s imperative to meticulously assemble and maintain a comprehensive Driver Qualification (DQ) File for each of your commercial drivers, as mandated by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA). Included within these files should be detailed records such as the driver’s application for employment, motor vehicle records (MVRs), a copy of the commercial driver’s license (CDL), documentation of medical examiner’s certificate, and records of any road tests conducted. The DQ file serves as a testament to a driver’s eligibility to operate commercial motor vehicles and must be updated with regularity to ensure ongoing compliance with DOT regulations.
Required Documentation
Under DOT regulations, operators must compile a faultless set of critical documents. Being meticulous here isn’t just advised—it’s a regulatory necessity to preempt any compliance issues down the line.
Since December 2015, the adoption of the Electronic Logging Device (ELD) mandate has necessitated carriers to equip their fleets with ELDs for recording driver’s Hours of Service (HOS), unless specifically exempt. This shift underscores a broader trend towards digitization and precision in compliance documentation.
It’s also essential to maintain an up-to-date Vehicle Maintenance File for every truck in your fleet. This record chronicles every inspection, repair, and maintenance activity, which not only ensures compliance but also promotes safety and operational reliability on the road.
Among the web of requirements, the annual DOT inspection certificates stand out. Proof of these inspections, the filing of accidents reports—if any, and the appropriate HazMat documentation, if relevant, are crucial. They’re part of the binding threads that uphold the fabric of road safety and compliance.
Failure to possess the correct permits, or a lapse in the renewal of operating authority, can bring about severe consequences. Therefore, vigilance in managing expiration dates and regulatory updates is indispensable to averting preventable interruptions in service.
Maintaining Records
Accurate record-keeping is the cornerstone of DOT compliance for flatbed trucking operations.
- Driver Qualification Files (DQF) including licenses, medical certificates, and road test results.
- Hours of Service (HOS) Logs for tracking driving hours, breaks, and rest periods.
- Maintenance and Inspection Records such as repair history, annual inspections, and preventive maintenance schedules.
- Accident Reports for every incident, regardless of severity.
- Hazardous Materials Documentation for any cargo classified as HazMat.
Not only does meticulous documentation support compliance, but it also significantly enhances safety protocols.
Adhering to retention schedules is essential — some records must be kept for a specific duration, often years after their creation.
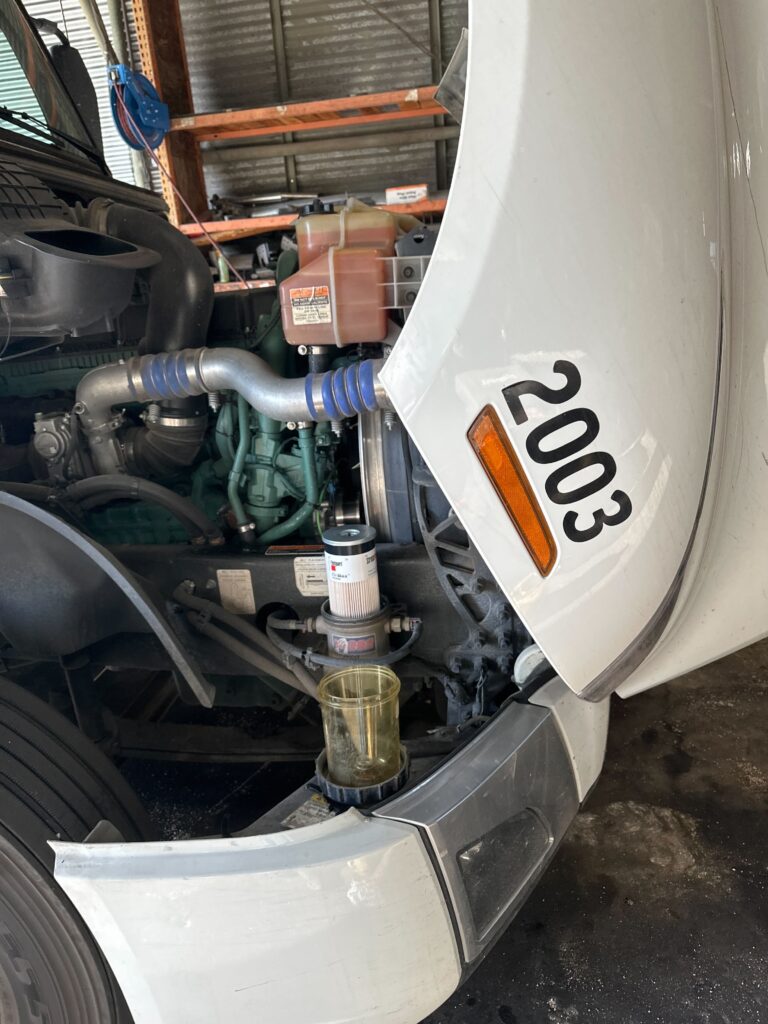
Vehicle Maintenance Standards
Maintaining stringent inspection protocols is crucial for operational safety and regulatory adherence in flatbed trucking. These standards ensure that vehicles remain safe and serviceable, preventing on-road failures that could have catastrophic outcomes.
A well-structured Preventive Maintenance (PM) program adheres to the Department of Transportation (DOT) regulations by scheduling regular upkeep, addressing service intervals, and maintaining detailed records of each action taken. A robust PM program is not merely a recommendation but a rigorous necessity to ensure the longevity and reliability of your fleet.
All components deemed “safety-sensitive” by the DOT must undergo stringent scrutiny. This means regular checks on braking systems, tires, lighting, and cargo securement devices among others, to maintain the highest safety benchmarks as mandated by federal regulations.
Routine Inspection Protocols
Adherence to DOT regulations demands thorough and regular inspections of all flatbed equipment and cargo securement.
- Inspect brake systems for proper operation and wear
- Examine tire condition, including tread depth and inflation
- Check lights and reflectors for functionality and visibility
- Verify cargo securement devices for integrity and appropriateness
- Review steering mechanisms for responsiveness and lack of excess play
- Assess fuel system for leaks and proper securement of components
- Confirm safe loading and adherence to weight limitations
- Evaluate emergency equipment for presence and serviceability
- Validate windshield wipers for functionality in inclement weather
- Perform undercarriage examinations for structural integrity
Properly documented inspection findings are the backbone of compliance.
Ongoing vigilance in inspection routines sustains peak performance and ensures regulatory conformity within your fleet operations.
Repair and Service Logs
Maintaining comprehensive repair and service logs is essential for complying with DOT regulations and safeguarding fleet operations. Detailed records exemplify a commitment to equipment integrity and road safety.
Proactive maintenance schedules are central to your operational excellence.
A meticulous record-keeping system demonstrates proactive measures to ensure fleet reliability and compliance with federal standards. Such documentation must be precise and up-to-date.
Logging repairs real-time prevents discrepancies and enhances traceability of the services performed. This organization reinforces a culture of accountability and operational transparency within your team.
When a discrepancy in your logs appears, tackle it immediately to avoid complications during DOT inspections, preserving your compliance record. A rigorous approach to repair and service logs prevents potential operational setbacks and underscores your dedication to safety.
Mitigate risks by auditing your logs regularly, ensuring they align with DOT regulatory requirements. Efficient record management can be a decisive factor in passing inspections with flying colors and dodging costly violations.
Complying with HOS Rules
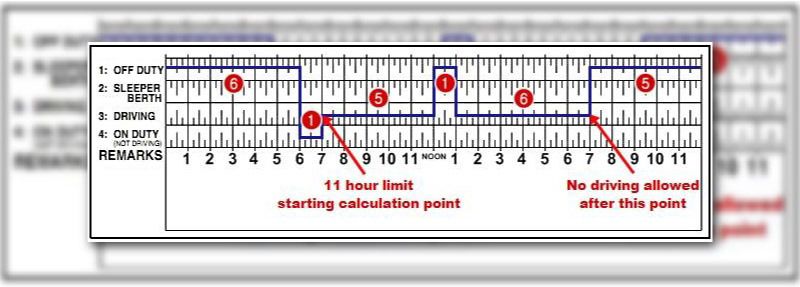
Ensuring adherence to Hours of Service (HOS) regulations is imperative for maintaining DOT compliance and promoting highway safety. Drivers must rigorously track their driving, on-duty, and rest periods to prevent violations of the federally mandated drive time limits. Precise logging, either through manual methods or electronic logging devices (ELDs), is non-negotiable to comply with HOS rules. Therefore, it is crucial for drivers to regularly review and comprehend these regulations, as non-compliance can result in significant fines and operational disruptions. Moreover, staying current with any updates or changes to HOS regulations is an ongoing responsibility for all flatbed trucking professionals.
Implementing ELDs
Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) are essential for HOS compliance, safeguarding authentic log creation. Install ELDs across your fleet to seamlessly monitor and report driver activity.
Since the ELD mandate was enacted, ensuring that every commercial vehicle is equipped with a compliant device has been crucial. These devices synchronize with the vehicle’s engine, capturing data accurately and automatically to reflect driving time.
As a flatbed trucking professional, familiarize yourself with the ELD interface and functionalities. A comprehensive understanding ensures accurate log maintenance, vital for DOT inspections and avoiding violations.
When selecting an ELD solution, prioritize systems certified by the FMCSA. Additionally, ensure that devices meet technical specifications and provide data in a standardized format for easy inspection by authorities.
Finally, never underestimate the importance of training drivers on ELD operation. Instructing your team on proper ELD usage is a critical step in achieving DOT compliance and minimizing human error.
Managing Drivers’ Hours
Rigorous adherence to Hours of Service (HOS) regulations is a foundational aspect of DOT compliance. The HOS rules govern the duration that drivers can operate a commercial motor vehicle before a required rest period.
The Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) has established the HOS regulations to enhance road safety, prevent fatigue-related accidents, and ensure operators receive adequate rest. The use of Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) is mandated for the accurate tracking of these hours.
As such, it’s imperative to manage and monitor your drivers’ HOS meticulously. This involves conducting regular audits of ELD records, retaining logs for the required six-month period, and educating drivers on HOS regulations to ensure compliance.
One of the vital aspects of HOS management is being proactive in preventing violations. Implement policies that support drivers staying within HOS limits and offer tools to help drivers plan their trips according to these restrictions.
Continual education on the importance of HOS compliance is paramount. Emphasize to your drivers how adherence directly impacts their safety and the safety of others on the road, reinforcing the personal responsibility each driver has.
What goes in a DOT compliance binder?

How to Choose the Right Flatbed Trucking Company Near You
A DOT compliance binder contains all the necessary documents and records that demonstrate a trucking company’s compliance with the regulations set by the Department of Transportation. These binders are essential for maintaining proper legal and operational requirements.
In the DOT compliance binder, you will find documents such as the driver qualification file, which includes information about the driver’s qualifications, driving history, medical certifications, and training records. This file ensures that only qualified and properly trained drivers are operating the vehicles.
Another important component of the compliance binder is the vehicle maintenance file. This includes records of regular inspections, repairs, maintenance schedules, and maintenance history of the fleet. It ensures that the vehicles are in safe and working condition, meeting the regulations set by the DOT.
Additionally, the binder will contain records of hours of service logs, which track the number of hours a driver has been on duty, driving, and taking breaks. These logs are crucial for monitoring and enforcing regulations related to driver fatigue and ensuring compliance with maximum driving time limits.
The compliance binder may also include records of drug and alcohol testing, accident reports, vehicle registration, insurance documents, and other relevant paperwork.
It is important to note that the specific requirements for a DOT compliance binder may vary based on the type and size of the trucking company, as well as the specific regulations of the jurisdiction. It is essential for companies to regularly update and maintain their compliance binders to avoid penalties and ensure the safety and compliance of their operations.
















A DOT compliance binder is essential for trucking companies to stay organized and meet regulatory requirements. It includes driver qualification files, vehicle maintenance records, HOS logs, and drug/alcohol testing documentation.
[…] are non-negotiable in flatbed trucking. Adhering to regulations, such as those outlined in the DOT compliance checklist, prevents delays and fines. Connect Express LLC’s focus on safety in flatbed transportation […]