What is ELD in Trucking?
ELD stands for Electronic Logging Device, is essential in trucking.
These devices are engineered to record driving hours and ensure compliance with the Hours of Service (HOS) regulations by maintaining an accurate record of duty status. HOS regulations set the maximum amount of time drivers are allowed to be on duty, including driving and resting hours. Historically, these records were maintained manually, leading to potential errors and regulatory breaches.
ELDs replace paper logbooks.
By automatically recording data such as engine hours, vehicle movement, miles driven, and location information, an ELD guarantees precise and reliable logs. Consequently, drivers can focus more on the road, knowing that their compliance documentation is handled flawlessly.
Additionally, ELDs offer enhanced safety by promoting better rest periods, reducing driver fatigue, and minimizing the risk of accidents. Moreover, with streamlined reporting and fewer manual entries, companies can allocate resources more effectively, boosting productivity and operational efficiency.
In essence, the adoption of ELDs marks a significant stride towards modernizing the trucking industry, ensuring compliance, safety, and productivity. Their widespread implementation underscores the industry’s commitment to leveraging technology for a safer, more efficient future.
Purpose of ELD in Trucking
The primary aim is compliance.
Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) help ensure that drivers adhere to federal Hours of Service regulations. These regulations are crucial for maintaining a safe environment on the roads, making it imperative for drivers to follow them. With ELDs, not only are the recordings more accurate, but the entire process becomes more transparent and easily reviewable by enforcement agencies.
Second, ELDs enhance safety.
By automating the logging process, ELDs reduce errors.
They allow for better monitoring and compliance, thus supporting safer driving habits. This efficiency ultimately leads to fewer accidents and enhanced road safety.
Furthermore, the precision and automation provided by ELDs contribute significantly to operational efficiency. Companies can track their fleets in real-time, allocate resources more effectively, and minimize administrative burdens. This modern approach to maintaining logs is transforming the trucking industry, reinforcing its commitment to safety, compliance, and efficiency.
Features of ELD Devices
ELD devices come equipped with various functionalities. These features enhance the trucking experience by ensuring compliance, safety, and efficiency for drivers and companies alike.
One prominent feature is the automatic recording of driving time. Since 2016, mandatory implementation has standardized operations, but these devices bring additional convenience by reducing manual logging errors.
Real-time location tracking is another standout feature of ELDs. It provides companies with immediate insights into their fleet’s positions, helping optimize routes, improve fuel efficiency, and ensure timely deliveries.
Moreover, ELDs often include diagnostic capabilities. By integrating with a truck’s engine, these devices can alert drivers and fleet managers to potential mechanical issues, reducing downtime and maintaining operational integrity.
In summary, the features of ELD devices drive advancements in compliance, safety, and overall efficiency.
How ELDs Work

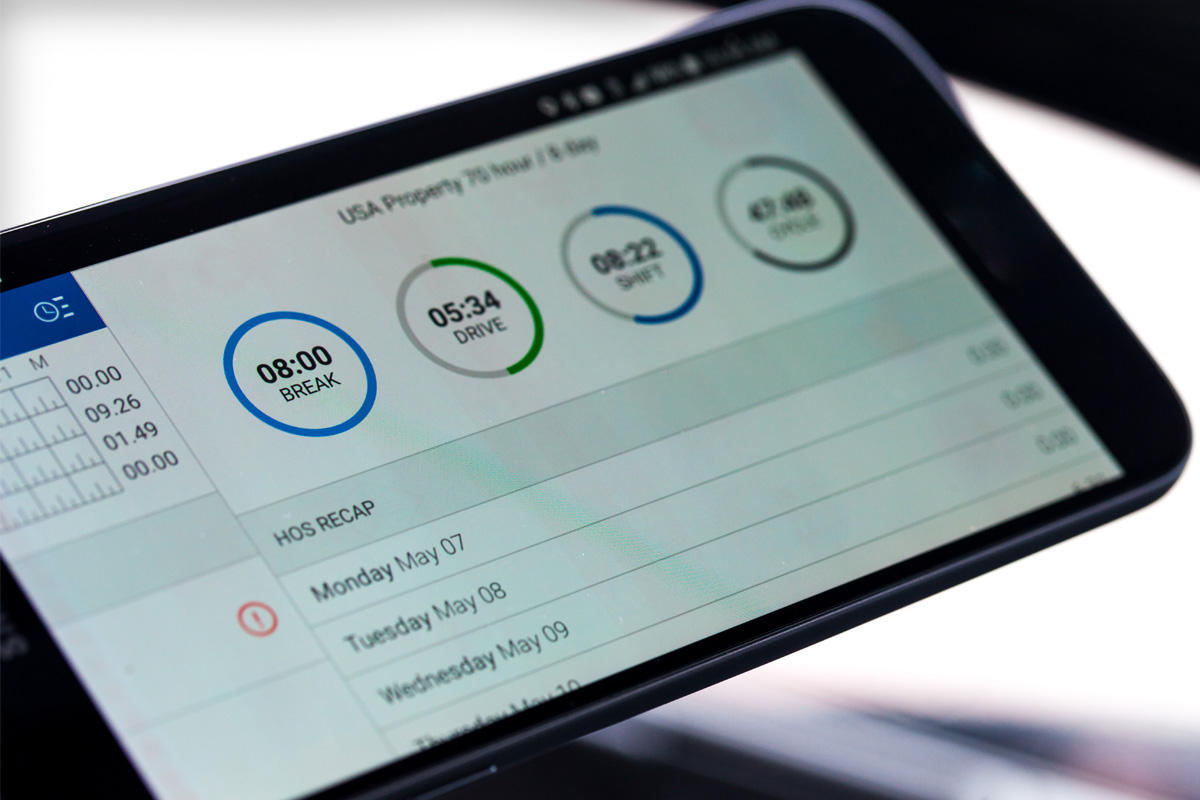
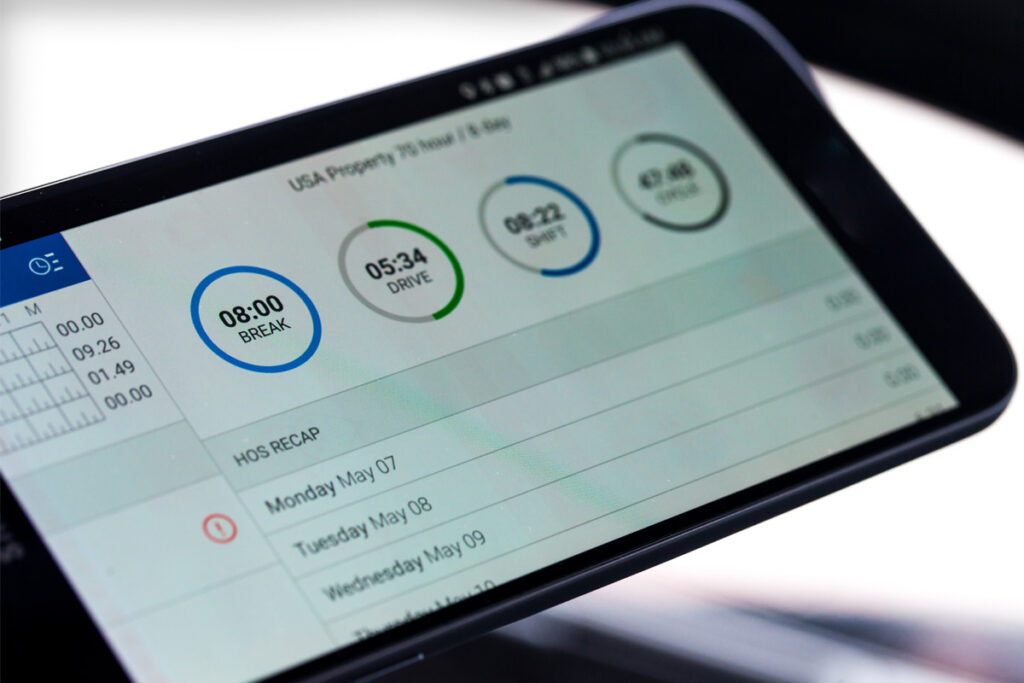
An ELD, or Electronic Logging Device, automates the recording of driving hours.
These devices, by seamlessly integrating with a vehicle’s engine, ensure accurate tracking of service hours, mileage, and location data. The integration allows for real-time data capture, which is then communicated directly to fleet management systems. This integration simplifies adherence to regulatory requirements while bolstering overall operational efficiencies.
Fundamentally, ELDs facilitate a streamlined communication process between the vehicle and management systems. By capturing essential data points, they provide a comprehensive overview of daily operations, thus empowering fleet managers to make informed decisions swiftly.
In essence, ELDs are invaluable in creating a culture of accountability and transparency within the trucking industry. They herald a new era of efficiency, underscoring the importance of technology in enhancing safety, compliance, and operational reliability. The continual evolution of these devices promises even greater advancements, illuminating the path to an optimized future in trucking.
FMCSA ELD Mandate Overview
Understanding what is ELD in trucking necessitates an exploration of the FMCSA ELD Mandate. Enacted by the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA), this mandate is pivotal.
The mandate enforces strict regulations on the use of Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs).
Implemented on December 18, 2017, the FMCSA mandate aims to enhance road safety. It seeks to ensure compliance with hours-of-service (HOS) regulations.
HOS regulations are crucial in preventing driver fatigue, which is a significant factor in road accidents.
The ELD mandate requires commercial truck drivers to replace traditional paper logs with electronic logs. This ensures a more accurate and tamper-resistant tracking system.
The benefits of the mandate extend beyond safety; it also drives operational efficiency. This regulatory evolution is a bold step towards a safer, more efficient, and transparent trucking industry.
Benefits of Using ELDs

Implementing ELDs in trucking offers a multitude of advantages that greatly enhance both safety and operational efficiency. By providing precise, real-time data, these devices empower fleet managers to make informed decisions, thereby optimizing route planning, fuel consumption, and overall fleet utilization. Moreover, accurate logging ensures compliance with HOS regulations, mitigating the risks of driver fatigue and reducing the likelihood of accidents.
Furthermore, digitizing logs eliminates the inefficiencies associated with paper logs. This transition fosters a streamlined workflow, minimizing administrative burdens and allowing companies to focus on core operational goals.
Improved Safety
Implementing Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) in trucks has profoundly enhanced safety—ELDs ensure precise monitoring of driver hours, crucial for preventing fatigue-related incidents.
A study showed a significant reduction in hours-of-service violations since the ELD mandate implementation.
By meticulously tracking driving hours, ELDs enable adherence to Hours-of-Service (HOS) regulations, substantially mitigating the threat of driver exhaustion and correlating with fewer accidents on the roads.
Additionally, ELDs facilitate instant access to driving records during inspections, reinforcing compliance and promoting a culture of safety throughout the trucking industry.
Enhanced Compliance
ELDs offer unmatched accuracy in logging hours, ensuring every driving minute is transparent and accountable.
This accuracy, in turn, translates directly to a meticulous adherence to regulatory standards, reducing the discrepancies and errors often associated with manual logs. The reliability fostered by ELDs ensures that trucking companies consistently meet the demanding benchmarks set forth by federal transportation authorities.
Furthermore, having comprehensive digital records readily available during inspections streamlines the review process. This instantaneous access to accurate data not only expedites inspections but also significantly reduces penalties arising from errors in logbooks.
Ultimately, ELDs have revolutionized compliance by enabling trucking businesses to uphold the highest standards of accuracy and accountability. This technological advancement elevates industry credibility, ensures seamless regulatory alignment, and fortifies the trust placed in the transportation sector by clients and the broader community.
Information Captured by ELDs
In trucking, ELDs encapsulate an array of critical data, ensuring steadfast compliance and monitoring precision.
Primarily, these advanced devices record a driver’s hours of service with remarkable accuracy, facilitating adherence to strict federal regulations. By systematically capturing detailed timestamps, ELDs provide an indisputable account of when a driver started and stopped working, essential for maintaining legal operational limits.
Additionally, they log vehicle movement, including location details at key intervals. This includes capturing precise geolocation data, which not only aids in route optimization but also verifies compliance with specified rest periods and driving durations.
Moreover, ELDs meticulously track engine hours, vehicle miles, and other diagnostic information, consequently bolstering vehicle maintenance schedules. By integrating real-time data, these devices empower trucking companies to enhance operational efficiency and foster a culture of safety and reliability within their fleets, in line with FMCSA regulations.
ELD Mandate Timeline
The journey towards the ELD mandate began with the necessity to bolster transparency in the trucking industry.
In 2016, federal legislation, a landmark directive fostering innovation, mandated that commercial motor carriers integrate ELD technology, initiating sweeping changes across the industry.
By 2017, it was clear that compliance was not optional, implementing deadlines became pivotal. The primary deadline encapsulated key benchmarks when vehicles and fleets transitioned to ELDs for enhanced transparency and accountability.
With the onset of the final phase, those in possession of older, grandfathered technology had until December 2019 to upgrade to new ELD systems, ensuring standardization and broader compliance.
This comprehensive timeline underscores steady advancements, reinforcing the industry’s unwavering commitment to safety, efficiency, and regulatory adherence.
Which Vehicles Need ELDs?

The ELD mandate primarily targets commercial motor vehicles, focusing on large trucks and buses. Specifically, operators who are currently required to maintain Records of Duty Status (RODS) must comply, ensuring their vehicles are equipped with a compliant ELD to accurately manage their record of duty status. However, certain exemptions exist for short-haul drivers and vehicles manufactured before 2000, allowing some flexibility while emphasizing the necessity of electronic logging in the modern transportation landscape.
Weight and Passenger Criteria
Determining which vehicles need an ELD also involves specific weight and passenger criteria. Intricately, a vehicle’s Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR) must exceed 10,000 pounds.
Such specifications intimately define the scope of ELD requirements within the trucking industry. Similarly, vehicles designed or used to transport more than eight passengers for compensation are included.
Ensuring compliance across these parameters signifies a forward-thinking approach to operational efficiency. Consequently, the same applies to vehicles designed to carry 16 passengers or more, even when not for compensation.
This comprehensive inclusion ensures that passenger safety and driver accountability are consistently prioritized. Hence, it is not just a measure for freight-heavy trucks but extends to larger passenger vehicles.
Adhering to these criteria, the industry effectively upholds high standards of safety and regulatory compliance. Ultimately, this meticulous approach fosters a robust, accountable, and safe transportation environment.
In essence, vehicles falling within these weight and passenger parameters are integral to the ELD mandate’s success. This ensures a unified framework driving the industry forward with unwavering diligence.
Exemptions to the ELD Mandate
Certain drivers, including those operating within short-haul regulations, are exempt from the ELD mandate requirements.
In addition, drivers who maintain records of duty status (RODS) for eight days or fewer within a 30-day period, are not subject to ELD usage.
Also exempt are drivers of vehicles manufactured before the year 2000. This exclusion acknowledges varying technological capabilities.
Paper Log Usage
Before the advent of Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs), drivers relied heavily on paper logs to record their hours of service.
- Completed by hand
- Subject to human error
- Time-consuming to manage
- Lacked real-time updates
- Required physical storage and organization
Paper logs required meticulous attention to detail and strict time management. Any discrepancies could lead to compliance issues.
Today, the industry is swiftly transitioning from paper logs to ELDs, streamlining processes and enhancing accuracy.
Driveaway or Towaway Operations
Driveaway and towaway operations pertain to scenarios where a vehicle’s cargo is its own transportation.
In many instances, vehicles are delivered without using a traditional trailer.
For example, when new trucks need to be transported to dealerships, the act of driving them off the factory floor directly to their destination qualifies as a driveaway operation.
Similarly, towaway operations involve hauling vehicles—new or used—without cargo trailers. These vehicles traverse long distances under their own power or via tow, ensuring timely and safe delivery to their designated locations, thereby reflecting a unique blend of logistics and operational expertise.
Vehicles Made Before 2000
Vehicles manufactured before the year 2000 are generally exempt from certain regulations within the trucking industry.
- ELD Mandate Exemption: These vehicles are not required to have Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs).
- Technical Constraints: The older engines and electronic systems are incompatible with modern ELD technology.
- Operational Continuity: Many older trucks still play a crucial role in freight and logistics sectors.
This exemption allows operators of older vehicles to maintain their operations without incurring retrofit costs.
As a result, the trucking industry benefits from the continued utility of these dependable, albeit older, vehicles.
Required Paperwork for ELD Compliance
Electronic Logging Devices (ELDs) are essential to streamlining operations and ensuring compliance within the trucking industry.
Since 2016, federal regulations mandate that most commercial trucks utilize ELDs to electronically record hours of service (HOS). This measure enhances both safety and transparency.
To remain compliant, drivers must carry supporting documents proving adherence to HOS regulations. These include records of duty status (RODS), bills of lading, and shipping documents.
Furthermore, a user manual for the ELD, including troubleshooting instructions, must always be accessible. Failure to present these documents could result in fines.
Maintaining accurate and organized paperwork is paramount to achieving full ELD compliance and fostering trust and efficiency in transportation.













